C#
// Write your own code here.
VB.Net
` Write your own code here.
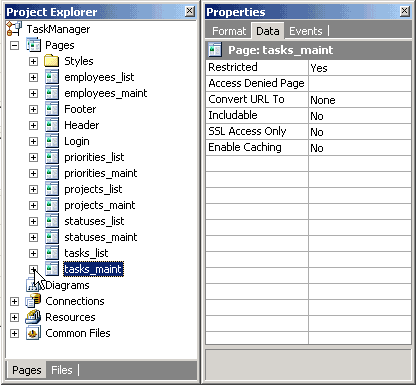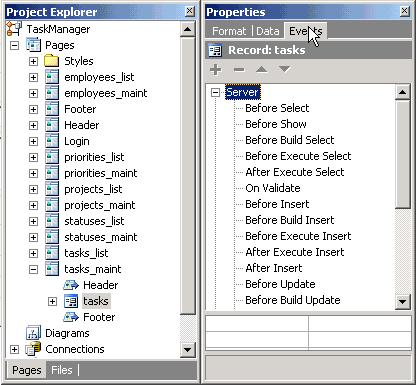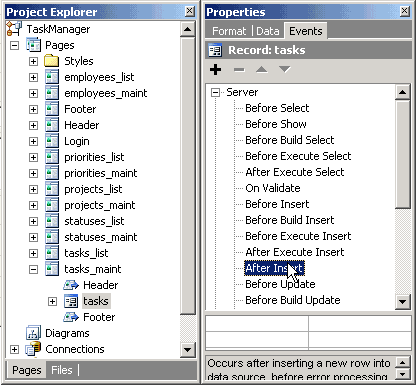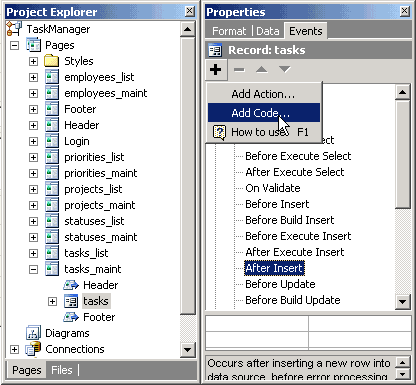
with the code below:
C#
Dim NewDao As DataAccessObject = Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject
if(ExecuteFlag&&!ErrorFlag){
SqlCommand userEmail = new SqlCommand( "SELECT email FROM " +
"employees WHERE emp_id=" + DBUtility.UserId,
Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject );
SqlCommand assignedUserEmail = new SqlCommand( "SELECT email FROM " +
"employees WHERE emp_id=" + item.user_id_assign_to.Value.ToString(),
Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject );
SqlCommand taskId = new SqlCommand( "SELECT max(task_id) FROM " +
"tasks WHERE user_id_assign_by=" + DBUtility.UserId,
Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject );
System.Web.Mail.MailMessage newMessage = new System.Web.Mail.MailMessage();
newMessage.From = userEmail.ExecuteScalar().ToString();
newMessage.To = assignedUserEmail.ExecuteScalar().ToString();
newMessage.Subject = "New task for you!";
newMessage.BodyFormat = System.Web.Mail.MailFormat.Html;
newMessage.Body = "The following task was submitted:<br><br>" +
"Task ID :"+ taskId.ExecuteScalar().ToString() +
"<br><br>"+ item.task_desc.Value;
System.Web.Mail.SmtpMail. SmtpServer = "localhost";
System.Web.Mail.SmtpMail.Send(newMessage);
}
VB.Net
If ExecuteFlag And (Not ErrorFlag) Then Dim userEmail, assignedUserEmail, taskId As String userEmail = Convert.ToString(Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject.ExecuteScalar( _ "SELECT email FROM employees WHERE emp_id=" & DBUtility.UserId)) assignedUserEmail = Convert.ToString(Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject.ExecuteScalar( _ "SELECT email FROM employees WHERE emp_id=" & Convert.ToString(item.user_id_assign_to.Value))) taskId = Convert.ToString(Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject.ExecuteScalar( _ "SELECT max(task_id) FROM tasks WHERE user_id_assign_by=" & DBUtility.UserId)) Dim newMessage As New System.Web.Mail.MailMessage() newMessage.From = userEmail newMessage.To = assignedUserEmail newMessage.Subject = "New task for you!" newMessage.BodyFormat = System.Web.Mail.MailFormat.Html newMessage.Body = "The following task was submitted:<br><br> Task ID :" & taskId & _ "<br><br>" & item.task_desc.Value System.Web.Mail.SmtpMail. SmtpServer = "localhost" System.Web.Mail.SmtpMail.Send(newMessage) End If
As you may have realized by now, the above code sends emails to users to whom the new tasks are assigned. Here is additional information you should be aware of:
- The above code use the classes provided by the .NET Framework to send e-mails, so you do not need to install extra components.
- The .NET Framework classes rely on the CDO component to send e-mails; hence you should need an SMTP service installed on the server hosting this application.
The following is an explanation of the above code.
if(ExecuteFlag&&!ErrorFlag){
SqlCommand userEmail = new SqlCommand( "SELECT email FROM " +
"employees WHERE emp_id=" + DBUtility.UserId,
Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject );
SqlCommand assignedUserEmail = new SqlCommand( "SELECT email FROM " +
"employees WHERE emp_id=" + item.user_id_assign_to.Value.ToString(),
Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject );
SqlCommand taskId = new SqlCommand( "SELECT max(task_id) FROM " +
"tasks WHERE user_id_assign_by=" + DBUtility.UserId,
Settings.IntranetDBDataAccessObject );
In the above code snippet three SqlCommand objects are defined. As you would remember, these objects are used to execute queries against the database. The first SQL query is used to retrieve the email address of the currently logged-in user. The second SQL query retrieves the email address of the user to whom the task is assigned. The user_id_assign_to property of the item object is used to get the user id of the user to whom the task is assigned. The last SQL query is used to get the task id. The last inserted task id can be obtained using different methods with different databases. Unfortunately, MS Access doesn't support the retrieval of the last inserted record; therefore you will need to use the SqlCommand object to lookup the largest task id submitted by the current user (assuming that task ids are created
incrementally).
System.Web.Mail.MailMessage newMessage = new System.Web.Mail.MailMessage();
Creates a MailMessage object, which is under the namespace System.Web.Mail.
newMessage.From = userEmail
newMessage.To = assignedUserEmail
newMessage.Subject = "New task for you!"
newMessage.BodyFormat = System.Web.Mail.MailFormat.Html
newMessage.Body = "The following task was submitted:<br><br> Task ID :" & taskId & _
"<br><br>" & item.task_desc.Value
The above code executes the query against the database and sets the various properties of the MailMessage object. Set the "BodyFormat" property of the MailMessage object to Html so HTML content can be sent (as opposed to plain text). The body of the email consists of the task description and the task id.
System.Web.Mail.SmtpMail. SmtpServer = "localhost"
System.Web.Mail.SmtpMail.Send(newMessage)
Set the address of the SMTP server which will be used to send the email then use the static Send method of the class SmtpMail to send the email. If you don't have an SMTP server on the local machine, you can enter the address of an external SMTP server which you have access to e.g. mail.yourdomain.com.
 CodeCharge Studio
CodeCharge Studio